fungi life cycle explained
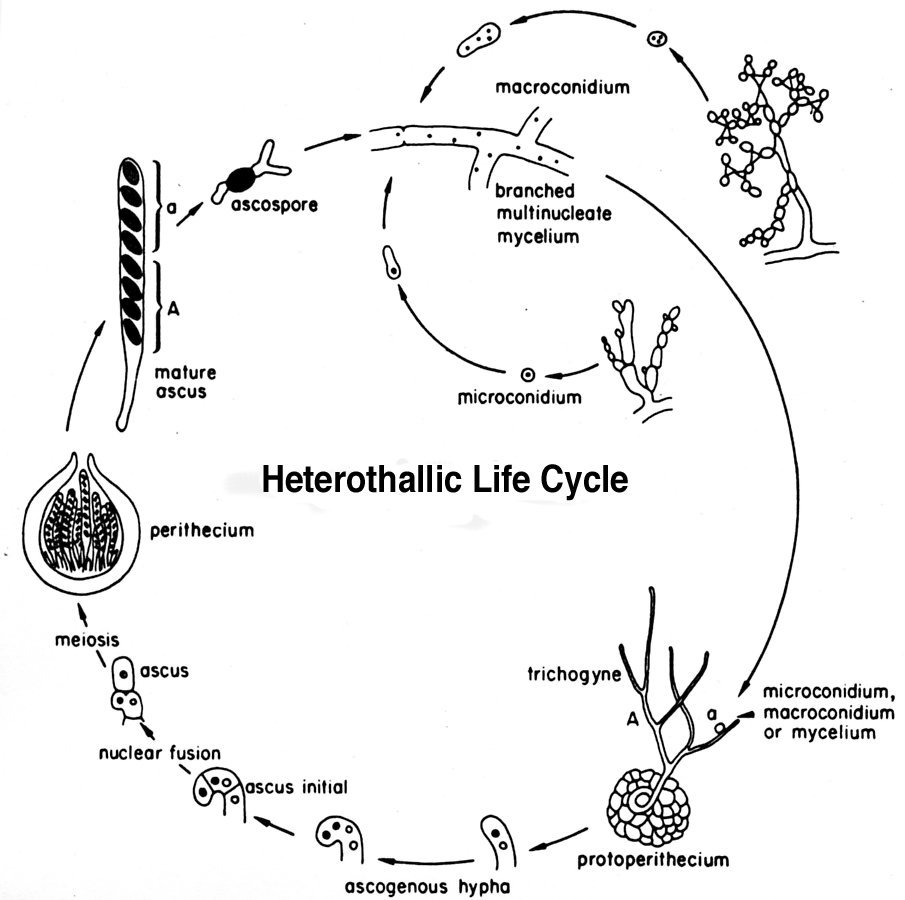
The fused hyphae containing haploid nuclei from two. The mycelium in most species of Taphrina is annual but in some species it is perennial.

Plasmogamy An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
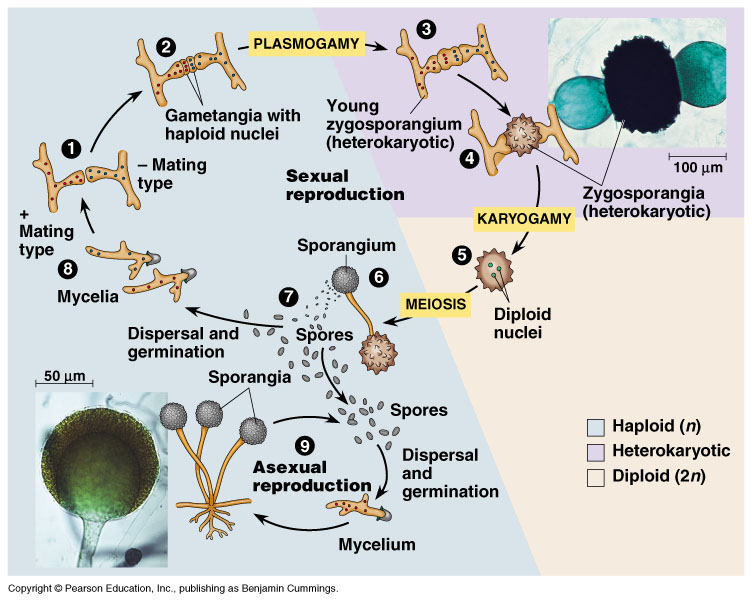
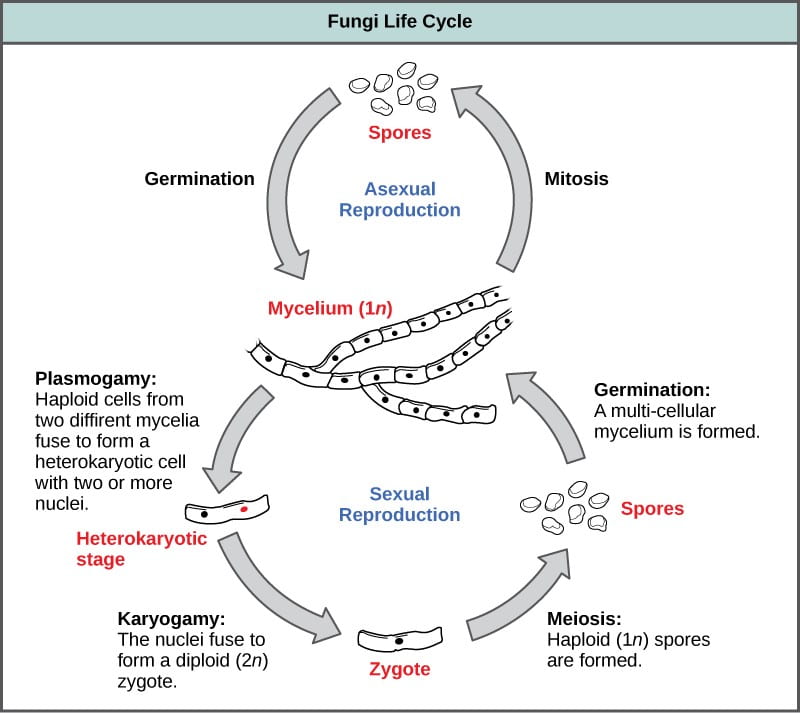
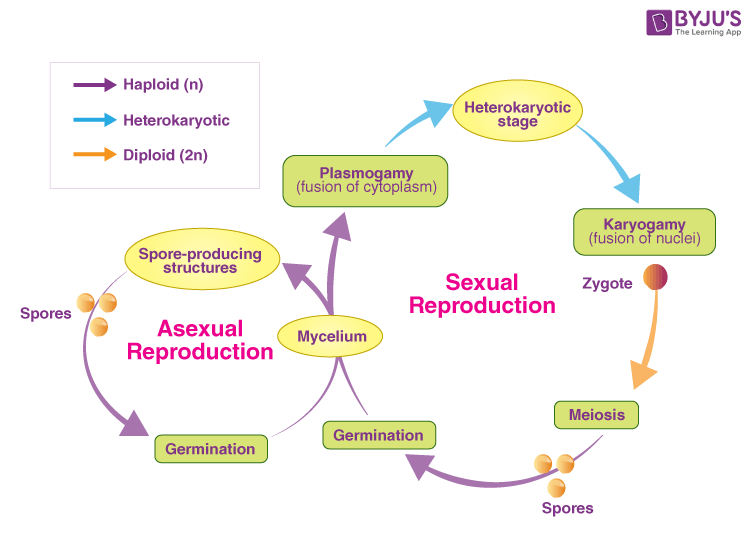
The haploid phase ends with nuclear fusion and the diploid phase begins.
. Asexual reproduction takes place by uninucleate thin-walled spores which are referred to as conidia. Some fungi are multicellular while others such as yeasts are unicellular. Fungi life cycle explained Wednesday March 2 2022 Edit.
How fungi are different from plants and actually are a lot more like animals this includes. Then through wind or air the spores go into the body and. In the life cycle of a sexually reproducing fungus a haploid phase alternates with a diploid phase.
The fungus spends most of its life cycle in this state and only forms mushrooms under specific conditions. 2022 Fungi Perfecti LLC PO Box 7634 Olympia WA 98507 USA. Most fungi are microscopic but.
Then these spores remain in a dormant state on the soil. Mushroom spores are tiny microscopic reproductive units that are produced by fungi as well as some. The whole life cycle of wood-loving macro-fungi from mushroom back around to mushroom.
Order Toll Free US Canada. Life cycle of fungi. Most of the ecology of the soil will die the plants do ok in the short run as they are able to absorb from the.
But first what even is a. Despite the name this doesnt. Fungi exhibit the phenomenon of alternation of generation.
If this is a. In these cells genetic material from the parent fungi combines and divides to form spores. Under favourable conditions each conidium germinates by germ tube which ultimately grows into somatic mycelium of the new individual.
The Life Cycle of Fungi 1. There are four basic steps in the life cycle of a fungi. The mushroom life cycle can be broken down into five stages.
Fungi are eukaryotic organisms and include yeasts moulds and mushrooms. Their role is to produce and release spores the fungal equivalent to. These spores also contain enough nutrients to support germination when it occurs.
The Life Cycle Of A Mushroom. This is how the fungus reproduces asexually. First the spores detach from the vegetative cell during adverse conditions.
The life cycle of a mushroom begins and ends through five stages of evolutionary phases beginning as a fungal spore seeds and completing its cycle as a mature fruiting. Fungi are subdivided on the basis of their life cycles the presence or structure of their fruiting body and the arrangement of and type of spores reproductive or distributional.
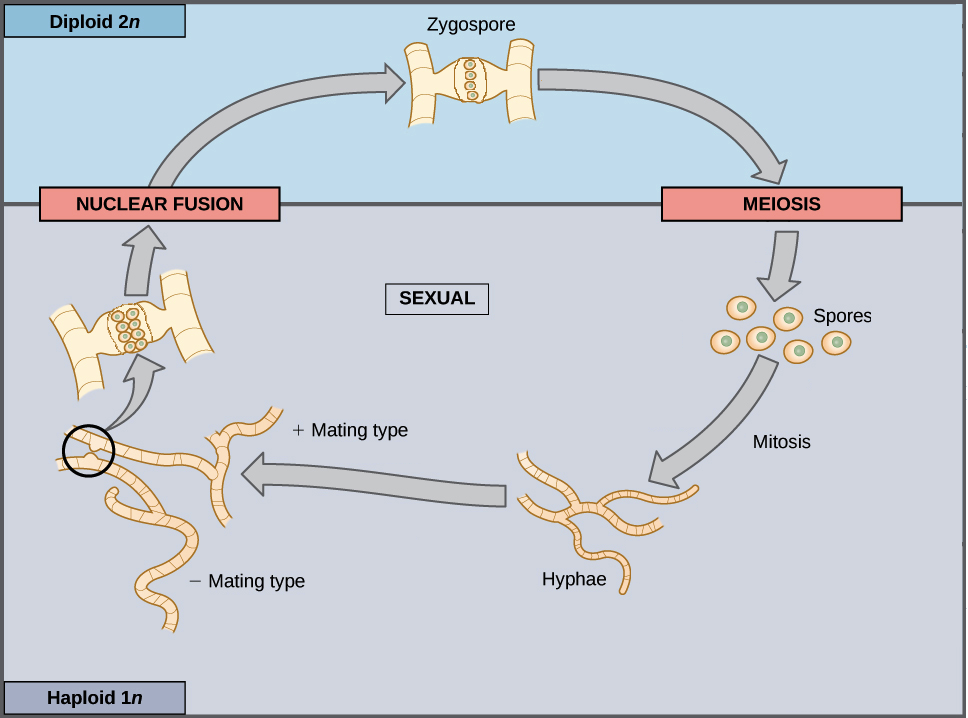
Sexual Life Cycles Article Meiosis Khan Academy
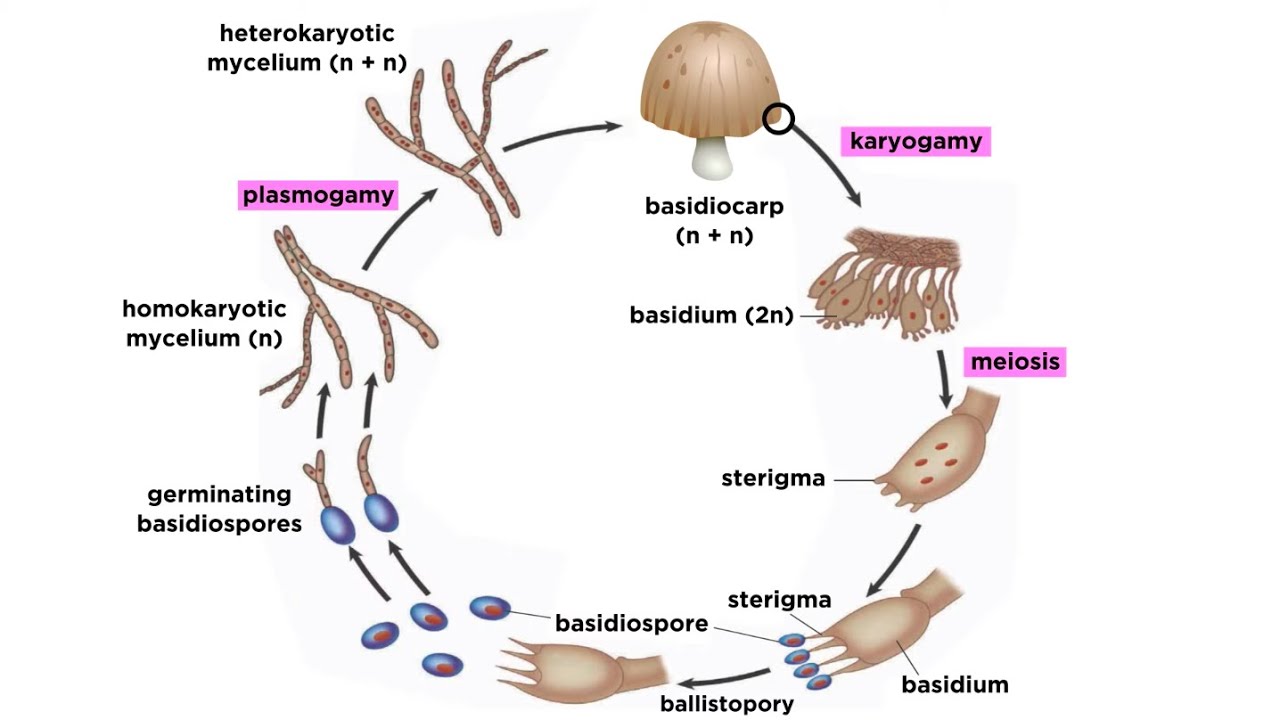
Basidiomycota Part 2 The Mushroom Life Cycle Youtube

24 1c Fungi Reproduction Biology Libretexts

Intro To The Fungi Life Cycle Plantsnap
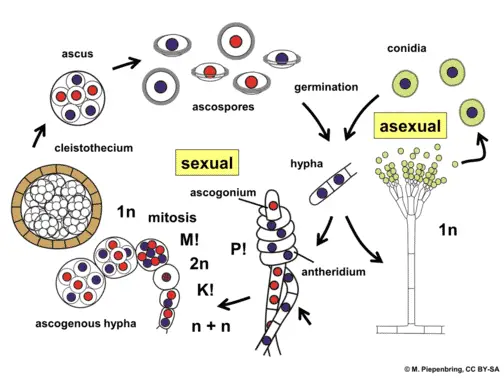
Fungi Explained Here Is What You Need To Know Microscope Clarity

Zygomycota The Conjugated Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Life Cycle Of An Am Fungus And The Different Steps During Am Development Download Scientific Diagram

Ascomycota The Sac Fungi Biology For Majors Ii

Biology Pictures Fungi Life Cycle 3 Life Cycles Fungi Biology

Diagrammatic Representation Of Mushroom Life Cycle Download Scientific Diagram

Fungi Life Cycle Introduction Life Cycle Faqs

A Detailed Explanation Of The Mushroom Life Cycle Grocycle

Life Cycle Of A Mushroom Worldkids
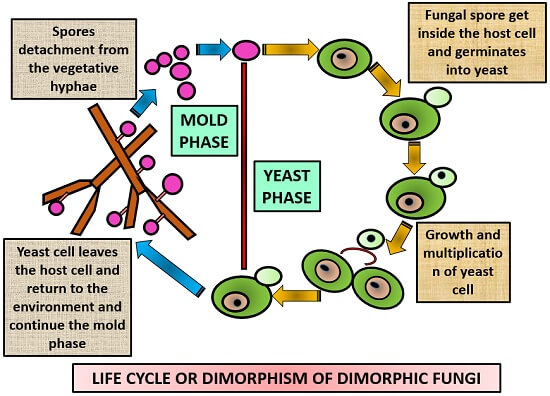
What Is Dimorphic Fungi Dimorphic Life Cycle Examples Transmission Biology Reader